
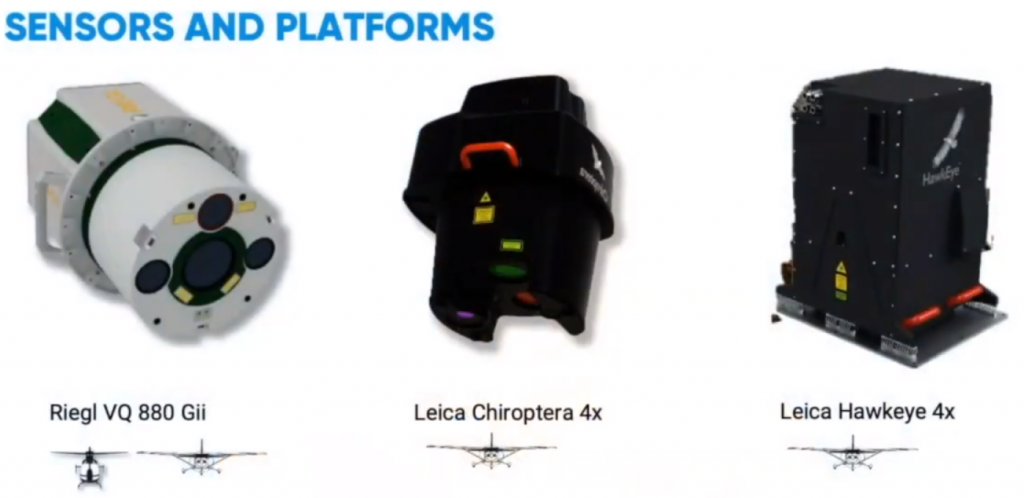
The 2020 Geolgnite conference was put online and brought the Canadian geospatial sector together. One of the topics included updates from the Quantum Spatial Canada as presented by its Program Manager, Mr. Sven Cowan.
Quantum Spatial is known for specializing in earth imaging using aerial platforms since 1930. At present, the organization has shifted significant focus to LiDAR. Watch the video as Quantum Spatial Canada discusses its innovative approach on forest trees classification and topobathymetry.
What is LiDAR imaging?
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) is a remote sensing technique that utilizes a pulse laser. This pulse laser reaches individual points on the ground and is reflected to platform sensor. The reflected pulse travel duration determines point distances, forms point clouds and generates the orthorectified image. Its spatial resolution is dependant on point density measured in point per square meter (ppsm).
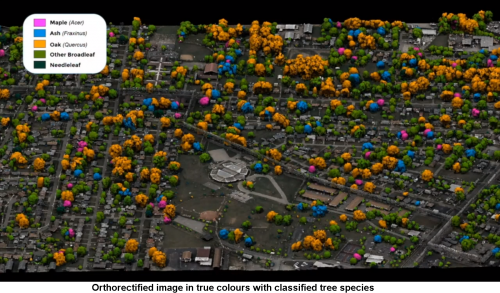
LiDAR-optical imaging tandem with the application of a machine learning algorithm to classify individual trees
Quantum Spatial Canada does a good job discussing its innovative method of using LiDAR-optical imaging tandem for mapping forest trees and individual tree species. This method grants us extensive opportunities to perform inventory of forested areas, which is valuable in environmental baselining, topographic survey of protected areas and reforestation activities. According to the Senior Program Director Dr. Andrew Brenner, the company acquires some forestry projects using both LiDAR and multispectral imagery platforms and then performs proprietary processing, which obtains pixel brightness intensity for every ground point. As a result, generated orthorectified images appear in true color.
Furthermore, the custom-built platforms are integrated with machine learning algorithm applications. This framework allows the classification of individual tree species on an orthorectified image in true color. The algorithm, which is now established in remote sensing spatial analysis, requires the collection of huge quantity of tree samples to be used as training data. Presently, the company is collecting thousands of samples of trees, to characterize their colors and structures.
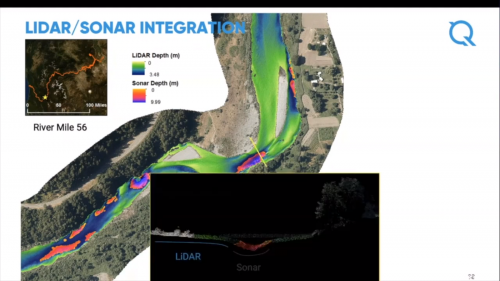
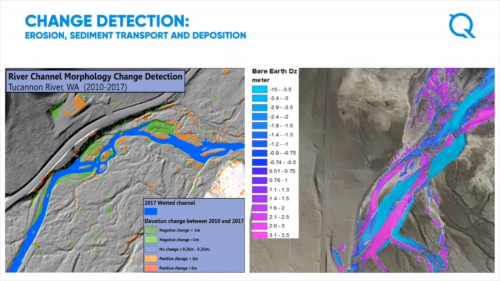
Topobathymetric LiDAR Survey
Mr. Colin Cooper, Senior Technical Domain Expert of Quantum Spatial, discusses the company’s topobathymetric LiDAR framework that eliminates image void interpolations as method of generating seamless full resolution LiDAR datasets. To make this work, green wavelengths are used to map the submerged water column whereas those sections covered with turbid water are done with sonar mapping. These features effects on a topographic Digital Elevation Model (DEM) are demonstrated by the image slideshow below and their distinctive contribution as well.

Topobathymetric LiDAR survey is valuable in submerged regions like benthic zones and earth dams. Other applications comprise project site characterization, engineering constructions and design, earth dam volumetric analyses, urban planning in flood-prone territories and quantifying benthic habitats. Presently, the company participates in shoreline mapping project of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in the United States. The project covers areas left unmapped since 1800s. This project aims covers the following; (a) Defining the US territorial limits; (b) Assisting on national coastal resource management; and (c) Providing spatial datasets to establish coastal flood models and emergency response plans.











Be the first to comment