
The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) has released a second report in the series called Failure to Act. The first in the series dealt with transportation.
Drinking water
The ASCE points out that water services in the U.S. are decentralized. There are about 170,000 public drinking-water systems, more than half of which serve fewer than 500 people. 54,000 of the water systens are community owned and provide water to more than 264 million people. The other 114,000 are non-community water systems, such as those for campgrounds and schools.
Most of the drinking-water infrastructure, but especially in older cities, is aging. When water systems fail, people are without water, emergency response is impeded, and there can be damage to other types of essential infrastructure. In the worst case water shortages may result in unsanitary conditions and public health issues.
Wastewater
According to the ASCE in 2008 there were about 14,780 wastewater treatment facilities and 19,739 sewer systems About 98 percent of publicly owned treatment systems were municipally owned. Aging pipes and inadequate capacity (SSOs and CSOs) result in the discharge of an estimated 900 billion gallons of untreated sewage into surface waters each year.
Capital investment
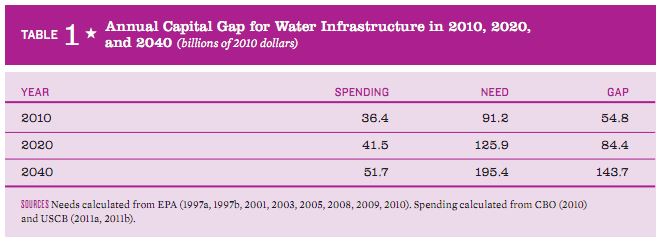 Acording to the EPA the capital investment required to maintain and upgrade U.S. drinking water and wastewater treatment systems in 2010 was $91 billion, but only $36 billion of this was funded, resulting in a capital funding gap of $55 billion. According to the ASCE, if this trends persist, by 2020 the funding gap will be $84 billion. By 2040 the funding gap will be $144 billion. With current trends addressing the gap will become increasingly more expensive, and waters will be polluted.
Acording to the EPA the capital investment required to maintain and upgrade U.S. drinking water and wastewater treatment systems in 2010 was $91 billion, but only $36 billion of this was funded, resulting in a capital funding gap of $55 billion. According to the ASCE, if this trends persist, by 2020 the funding gap will be $84 billion. By 2040 the funding gap will be $144 billion. With current trends addressing the gap will become increasingly more expensive, and waters will be polluted.
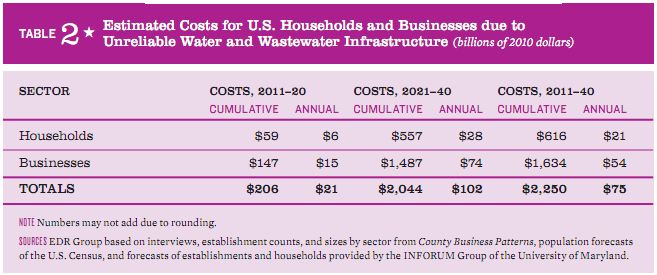 The ASCE report estimates the impact of not addressing the funding gap will have on househilds and businesses and on the national economy. The major impacts will be
The ASCE report estimates the impact of not addressing the funding gap will have on househilds and businesses and on the national economy. The major impacts will be
- Water shortages will result in higher rates and major outlays by businesses and households, including expenditures to move to where infrastructure is still reliable; purchasing and installing equipment to conserve water or recycle water; and increasing reliance on self-supplied water and wastewater treatment.
- Increased medical costs as a reult of increases in water-borne illnesses.
 The estimated expenses to businesses of unreliable water delivery and wastewater treatment is estimated to be $147 billion by 2020, and $59 billion for households. The total impact of increased costs and reduced income will decrease the standard of living for families by almost $900 per year by 2020.
The estimated expenses to businesses of unreliable water delivery and wastewater treatment is estimated to be $147 billion by 2020, and $59 billion for households. The total impact of increased costs and reduced income will decrease the standard of living for families by almost $900 per year by 2020.
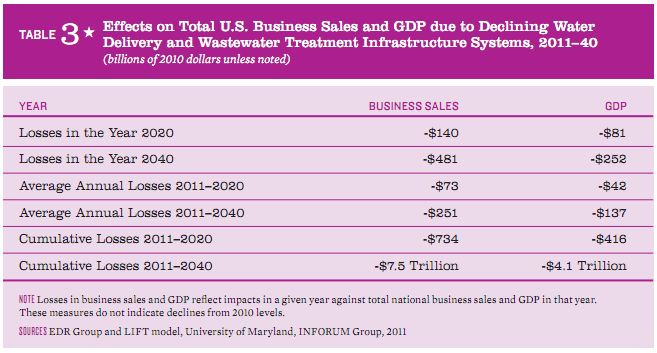
By 2020, the predicted deficit for sustaining water delivery and wastewater treatment infrastructure will be $84 billion. In a worst case scenario, the U.S. will lose nearly 700,000 jobs by 2020 and 1.4 million jobs by 2040. Between now and 2020, the cumulative loss in business sales will be $734 billion and the cumulative loss to the U.S. GDP will be $416 billion. By 2040, the impact will be $481 billion in lost business sales and $252 billion in lost GDP.


Be the first to comment