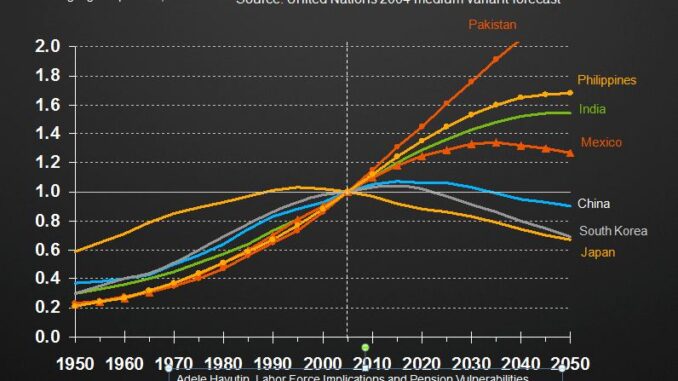
As I blogged previously there were several very important and topical presentations at the GITA conference this year addressing the challenge of the aging workforce. The problem is severe in many of the world’s economies, but especially in Japan which has the highest proportion of citizens over the age of 65, about 23% of the population. The population of Japan is declining and there is data that suggests this trend is accelerating. The National Institute of Population and Social Security Research has estimated that Japan’s population will drop to below 100 million by 2046.
Japan is also facing the same challenges that other advanced economies are plus some unique to Japan including renewable energy, safe nuclear power, increased broadband access, addressing sea level rise, intelligent networks/smart grid, water management, and rebuilding after the recent major earthquake and resulting tsunami. For Japan’s telecommunications and utility companies this means more things to do and fewer people to do them.
A related problem is the quality of the data in the facilities databases maintainted by utility and telecommunications companies. Historically network operators have managed to muddle along with data that can be up to several years out of date because of as-built backlogs and inaccurate because current business processes are not targetted on optimizing data quality, for example, operations staff are often not encouraged to report errors they see out in the field. But with the next generation of intelligent networks or smart grids, many in the industry believe that utilities and telecommunications firms are going to have to get serious about maintaining what one long time utility specialist calls “100% accurate, real time” facilities data.
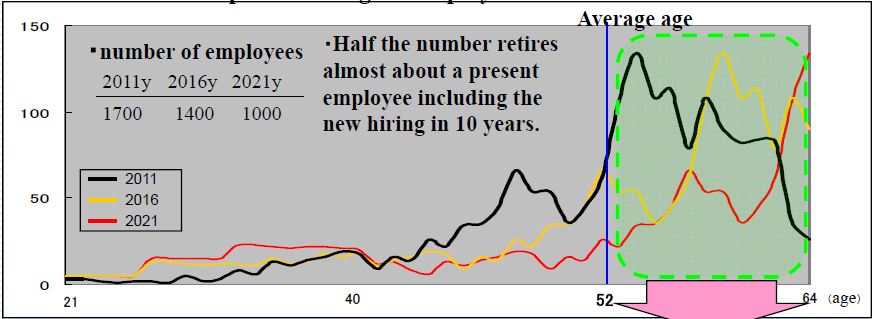 At the GITA conference this year, Toyokazu Fukui, Director of Development at NTT Infranet, described the workforce challenges at NTT Infranet. The size of the company’s workforce is expected to decline from its current 1700 employees to 1400 by 2016. In addition many employees are over 52 and about half will be eligible to retire in the next ten years. In his presentation Fukui-san describes how NTT Infranet has changed its data management practices and implemented an IT system to enable knowledge transfer from the older cohort of workers to the younger generation.
At the GITA conference this year, Toyokazu Fukui, Director of Development at NTT Infranet, described the workforce challenges at NTT Infranet. The size of the company’s workforce is expected to decline from its current 1700 employees to 1400 by 2016. In addition many employees are over 52 and about half will be eligible to retire in the next ten years. In his presentation Fukui-san describes how NTT Infranet has changed its data management practices and implemented an IT system to enable knowledge transfer from the older cohort of workers to the younger generation.
NTT Infranet realized that a critical requirement to acheve business benefits from a geospatially enabled facilities database is that the data be reliable and current. Some of the specific problems that Fukui-san mentioned NTT Infranet experienced with its first geospatial implementation include data quality issues resulting from delayed data entry, redundant data, a large headcount dedicated to data entry, data chronically out of date and unable to be used for day to day operations, and limited use across the organization. None of these are unfamiliar.
Fukui-san described how NTT Infranet is making it possible to capture the “knowhow” of experienced workers in the company’s facility database so that it can be accessed by all workers, especially younger, less experienced workers. The ciritical areas that NTT Infranet identified as priorities for enabling this to happen are (1) a single location aware infrastructure (logical) database containing all the company’s information about its facilities, (2) simplified data capture that enables faster and more timely entry of the data critical for business operations, and (3) adapting business processes to optimize data quality. With this approach NTT Infranet is realizing business benefits such as lower costs of operations. But this approach also provides a comprehensive, current view of network operations which enables the younger generation to suggest improved ways to do things that had not occurred to their seniors.


Be the first to comment