In contrast to the European Community which adopted the 20-20-20 legally binding agreement several years ago, the U.S. does not have a national clean energy standard (CES), though about 36 states have some form of RPS or RES.
The Energy Information Administration (EIA) has just released an assessment of the impact of a potential national CES as requested by the Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources. The policy assumptions were set out for the study by the Senate Committee.
The national CES would requires electricity retailers to supply a specified share of their electricity sales from qualifying clean energy resources. Electricity generators would be granted clean energy credits for every megawatthour (MWh) of electricity they produce using qualifying clean energy sources. The base CES specification (BCES) case defines clean energy, the allocation of credits, and the dates when target milestones become binding:
- All generation from existing and new wind, solar, geothermal, biomass, municipal solid waste, and landfill gas plants earns full BCES credits.
- Incremental hydroelectric and nuclear generation from capacity uprates at existing plants and from new plants earns full BCES credits.
- Generation from existing nuclear and hydroelectric capacity does not receive any BCES credits.
- Partial BCES credits are earned for coal and natural gas plants which capture and sequester their carbon dioxide emissions, new and existing natural gas combined-cycle units, new and existing gas combustion turbines, and integrated gasification combined-cycle (IGCC) coal plants without carbon capture.
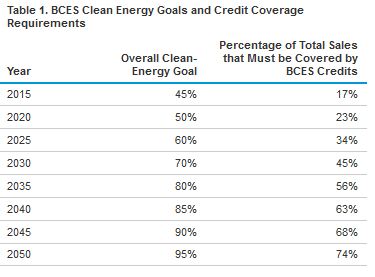
The BCES target for the share of retail electricity sales from clean energy sources starts at 45 percent in 2015 and ultimately reaches 95 percent in 2050. All electricity providers are covered by the requirement, regardless of ownership type or size. The BCES operates independently of any State-level policies such as a State RPS or RES. The BCES case is compared to the IEA’s annual energy outlook for 2011 AEO2011 reference case.
BCES case impacts
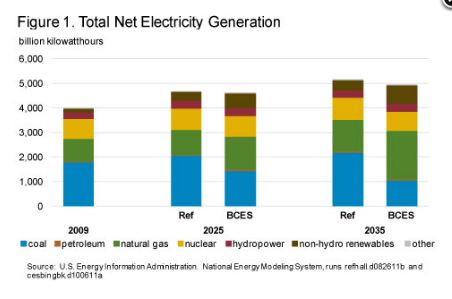 The BCES policy changes the generation mix, reducing the role of coal technologies and increasing reliance on natural gas, non-hydro renewable and nuclear technologies. Coal-fired generation decreases by 41 percent in the BCES case betwwen 2009 to 2035. Natural gas generation increases by 53 % in 2035. Non-hydro renewable generation grows at the fastest rate, becoming 75 percent greater in 2035 than in the AEO2011 projection. Nearly 65 GW of new nuclear capacity are installed by 2035. 14 GW of existing nuclear capacity are taken out of service. 47 GW of coal capacity is retrofitted with carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) equipment by 2035. Most of these retrofits occur in the final 10 years with less than one gigawatt of capacity retrofitted by 2025.
The BCES policy changes the generation mix, reducing the role of coal technologies and increasing reliance on natural gas, non-hydro renewable and nuclear technologies. Coal-fired generation decreases by 41 percent in the BCES case betwwen 2009 to 2035. Natural gas generation increases by 53 % in 2035. Non-hydro renewable generation grows at the fastest rate, becoming 75 percent greater in 2035 than in the AEO2011 projection. Nearly 65 GW of new nuclear capacity are installed by 2035. 14 GW of existing nuclear capacity are taken out of service. 47 GW of coal capacity is retrofitted with carbon capture and sequestration (CCS) equipment by 2035. Most of these retrofits occur in the final 10 years with less than one gigawatt of capacity retrofitted by 2025.


Be the first to comment