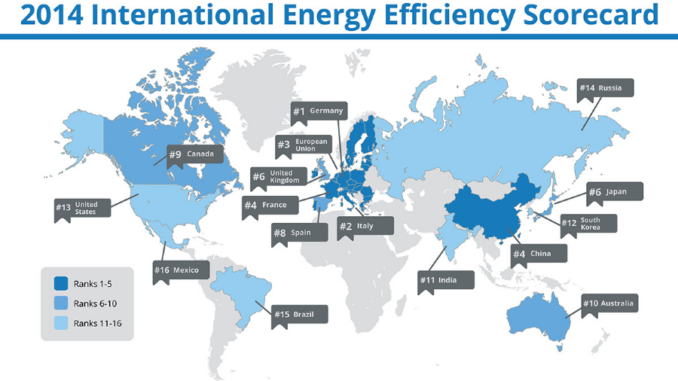
According to the 2014 scorecard released by the American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (ACEEE) Germany is #1 out of the 16 nations studied in the World for energy efficiency. In Germany buildings currently account for 40 percent of power consumption and a third of CO2 emissions.
Energy efficiency of buildings
In September 2010 the German Government released a 40 year masterplan for revolutionizing the German energy supply that includes an aggressive plan for energy conservation focusing on reducing the energy demand from buildings. According to the plan new insulation standards are to be introduced the government wants all buildings in Germany to be refurbished in line with new standards by 2050. It also wants to cut the national heating requirement by 20 percent by 2020 and by 80 percent by 2050. Germany is part of the EU which is very aggressive in improving the energy efficiency of buildings. The EU Energy Saving Ordinance mandates a 25 percent reduction in energy use for all new residential and non-residential buildings built from January 1, 2016. And as of 2021, the EU’s nearly zero energy standard will apply to all new buildings.
According to the ACEEE scorecard Germany is ahead of most countries in implementing energy conservation policies and measures for buildings. (The IEA provides a listing of German energy conservation policies and measures.) But Germany came in second to China in the ACEEE assessment of its progress in improving the energy efficiency of buildings. The ACEEE assessement focussed on several criteria for building efficiency including energy intensity in residential buildings, energy intensity in commercial buildings, residential building codes, commercial buildings codes, building labeling, appliance and equipment labeling, and building retrofit policy.
The EIA has just released information on building energy efficiency programs in China. Unlike many other countries, the Chinese government has focused a lot of regulatory attention on existing buildings. The overall objective of the Chinese government is to raise the level of existing buildings to satisfy regulations governing new construction. In 2011, the government implemented regulations that mandated a 10% reduction in energy consumption per square meter for commercial buildings by the end of 2015. It also mandated a 15% reduction for commercial buildings with more than 20,000 square meters of floor area. 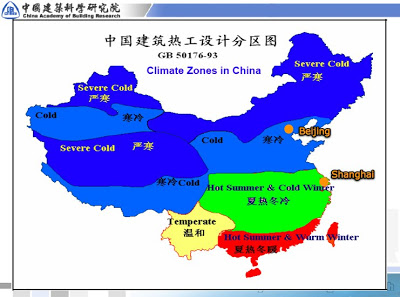
The Green Building Action Plan of 2013 mandates that more than 400 million square feet in residential homes in the northern heating zone must be refurbished to meet new construction standards by the end of 2015. (According to the World Bank 46% of residential floor area is in “severe cold” or “cold” regions.) In addition all commercial buildings in the same zone must be renovated to meet the standards by 2020.
Energy labeling
In 2006 China started a green building labeling initiative called Three-Star Rating Building System. This system required buildings to be assigned a rating of one to three stars using several criteria. These include land usage, energy and water consumption, material efficiency, indoor environmental quality, and operational management. The Three-Star Rating Building System departs from the LEED standard in assigning categories based not only on a building’s design but also on the building’s performance over one year of operation.
Appliance and equipment labeling
China began an energy efficiency labeling program in 1998 with a voluntary energy efficiency labeling program. Then in 2005, a mandatory energy information label was introduced that assigned appliances to categories based on their energy efficiency. This program is similar to the European Union categorical energy label.
Green building codes
In 1986 China issued the first building energy code in 1986 for residential buildings in the northern heating zone. These regulations mandated a 30% reduction in space heating energy consumption compared with 1980 reference buildings. For each of China’s four climate zones (severe cold or cold climate, hot summer/cold winter, and hot summer/warm winter), there are three energy codes for residential buildings. There is one code for commercial buildings. Regulations are mandatory except in rural area where 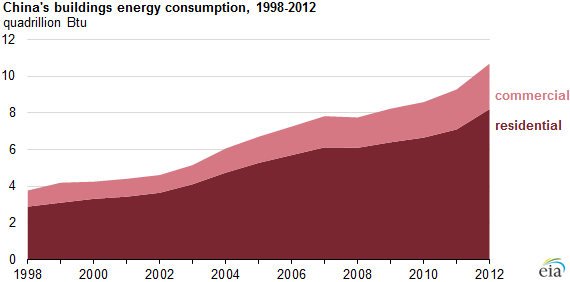 residential energy codes are voluntary.
residential energy codes are voluntary.
Even with these regulations, from 1998 to 2012 energy consumption of buildings in China grew by about 7.7% per year. This is ascribed to rapid economic development and the rapid rise in personal incomes in China during this period allowing people to acquire and use more appliances. In addition China’s buildings are inefficient compared to developed countries. It is estimated that buildings in China use 2-3x more energy per square meter for heating than buildings in comparable temperature zones in Europe or the US. Furthermore thermal comfort is significantly lower in China.


Be the first to comment