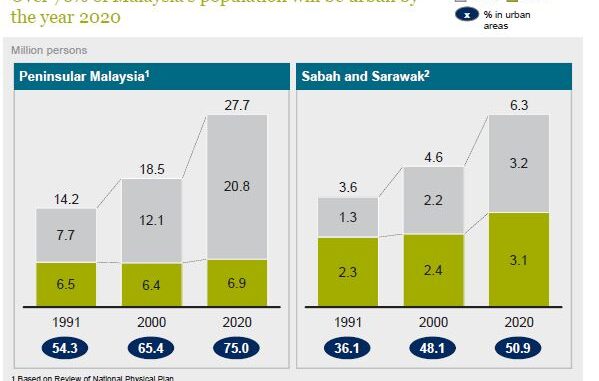
Malaysia expects that 70% of its inhabitants will be living in urban environments by 2020. Last year Malaysia released its 10th Malaysia Plan (10MP), which focuses on developing infrastructure to improve productivity and making the private sector the engine of development. The target is to make Malaysia a high income economy through productivity growth. One of the reasons the government wants to encourage urbanization is international empirical evidence that cities have three times the productivity of rural areas. MP10 identifies 12 National Key Economic Areas (NKEA), most of which are sectoral, but one of which is Malaysia’s largest urban centre Greater Kuala Lumpur.
The Malaysian economy has been very successful in the past, but primarily because it has been a low cost economy. The Malaysian electrical and electronics industry, which is known worldwide for inexpensive digital components, is responsible for 26.1% of manufacturing output and
more than 40% of total manufacturing labour.
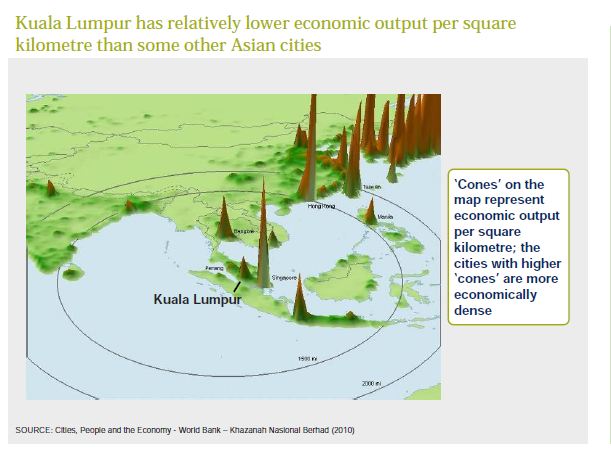 According to MP10, the Malaysian economy needs to improve productivity, by upskilling the existing work force to facilitate industries to move up the value chain, enabling specialization and economies of scale, and increasing public investment in innovation, particularly R&D and venture capital funding especially through shared risk public-private partnerships. The government has created a RM 20 billion (US$ 6 billion) Facilitation Fund that it hopes will attract RM 200 billion (US$60 billion) in private capital. ICT is a major area of focus for improving productiivity. ICT accounted for 9.8% of GDP in 2009 and is targeted to increase to 10.2% by 2015.
According to MP10, the Malaysian economy needs to improve productivity, by upskilling the existing work force to facilitate industries to move up the value chain, enabling specialization and economies of scale, and increasing public investment in innovation, particularly R&D and venture capital funding especially through shared risk public-private partnerships. The government has created a RM 20 billion (US$ 6 billion) Facilitation Fund that it hopes will attract RM 200 billion (US$60 billion) in private capital. ICT is a major area of focus for improving productiivity. ICT accounted for 9.8% of GDP in 2009 and is targeted to increase to 10.2% by 2015.
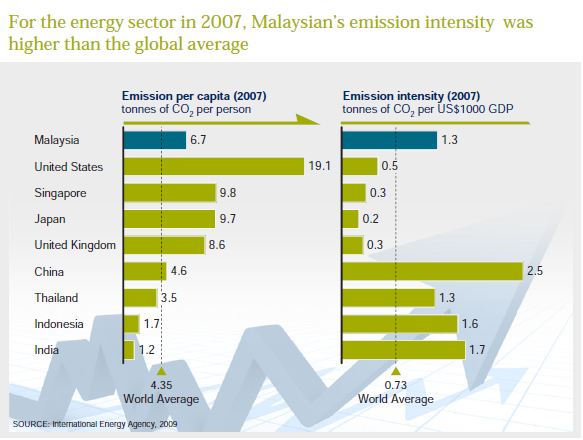 The MP10 focusses on development of infrastructure specifically housing, transportation, energy, water resources and sustainability. Major initiatives include increasing broadband penetration, upgrading transportation networks, ensuring a secure and reliable energy supply including increasing renewable energy, developing a long-term strategy for water resource management and restructuring the water services industry, protecting rivers from pollution, adaptation to protect Malaysia from the risks of climate change, and reducing Malaysia’s carbon footprint. I blogged previously about Malaysia’s recent introduction of a feed-in tariff program to encourage renewable energy and TNB’s smart grid plans to support distributed generation.
The MP10 focusses on development of infrastructure specifically housing, transportation, energy, water resources and sustainability. Major initiatives include increasing broadband penetration, upgrading transportation networks, ensuring a secure and reliable energy supply including increasing renewable energy, developing a long-term strategy for water resource management and restructuring the water services industry, protecting rivers from pollution, adaptation to protect Malaysia from the risks of climate change, and reducing Malaysia’s carbon footprint. I blogged previously about Malaysia’s recent introduction of a feed-in tariff program to encourage renewable energy and TNB’s smart grid plans to support distributed generation.
 The MP10 sees environmental management as an incipient industry with substantial growth potential in green technology which could spin off new categories of professionals and new areas of specialization for architectural and engineering services.
The MP10 sees environmental management as an incipient industry with substantial growth potential in green technology which could spin off new categories of professionals and new areas of specialization for architectural and engineering services.
The plan identifies 52 high impact infrastructure projects worth RM 63 billion including
- Seven toll highways – RM 19 billion
- Two coal-fired power plants – RM 7 billion
- Malaysian Rubber Board land development – RM 10 billion
- Electrified double track rail project – RM 8 billion
- Waste water treatment plant using green technology in Lembah Pantai
- Roads, electricity, water supply, and communication networks to rural areas
- Construction of 76,000 affordable houses


Be the first to comment