In my last blog I outlined some alternative architectures that a large organization could implement to share spatial information. In this blog I would like to present a practical example of the spatial warehouse architecture that adds an interesting wrinkle that may make this more universally applicable.
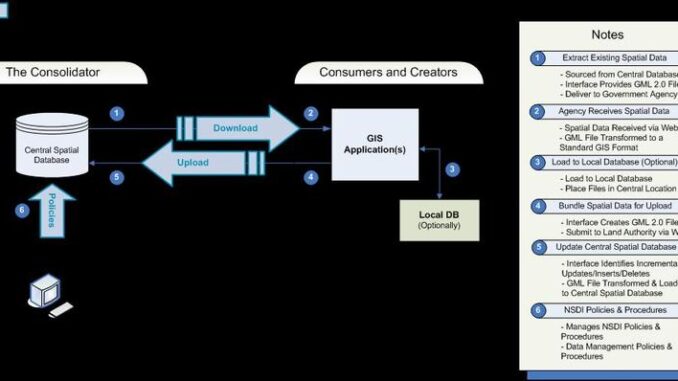
The workflow for this spatial warehouse architecture involves periodically uploading information from
the data sources (creators), and then providing a web interface to allow users (consumers) of this data to select and extract for download subsets of the data. I’ve included a diagram showing this workflow (again thanks to Bruce Argue for this.) This architecture corresponds to the standard IT architecture of a data warehouse. As I mentioned previously, the advantage of this approach is that it has minimal impact on the operational subsystems that own (create and manage) the data.
However, the most common issue with this approach is that of data format. Frequently, the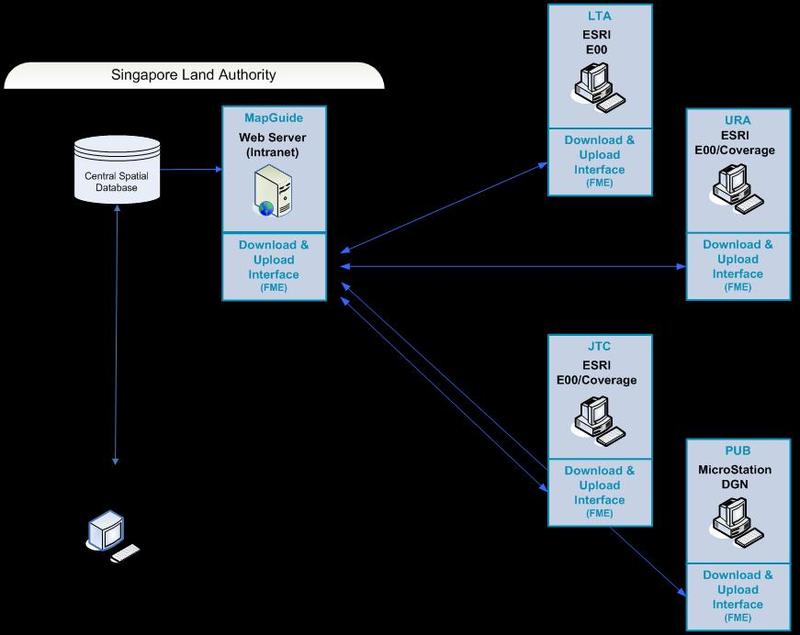
data creators are using an application from a geospatial vendor like ESRI, Autodesk, Bentley, MapInfo, Microsoft, or intergraph and likewise the consumers are using an application from a different vendor. Often WMS/WFS may not be supported by the creator or by the consumer. One way to get around this problem and provide universal access to everyone in the organization is to integrate Safe Software’s FME on the server and on the client. With FME the data can be converted on the upload and loaded into the spatial RDBMS (e.g., Oracle Locator/Spatial) and on the download to whatever format is appropriate for the consumer. This way access to the data is not restricted to WMS/WFS servers and clients, which are not yet universally supported.


Be the first to comment