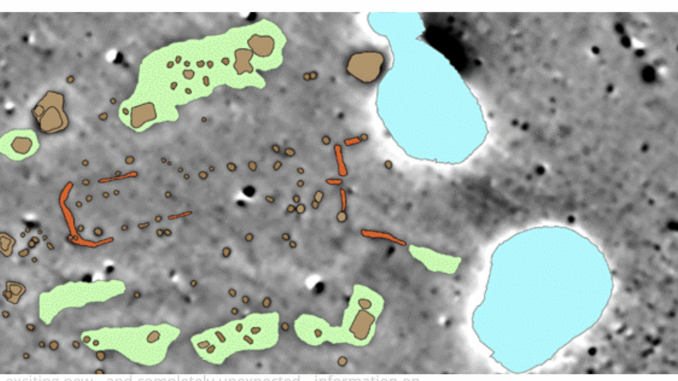
The objective of the remarkable four year Stonehenge project was to create a detailed archaeological map of Stonehenge and its surroundings based on a synthesis of remote sensing and subterrainean geophysical data. The result is a digital model of the Stonehenge landscape that ties surface features together in a seamless map with underground features and structures that shows that Stonehenge proper is only a small piece of a much larger, more complex ancient structure.
The Stonehenge Hidden Landscapes Project is led by the University of Birmingham in conjunction with the Ludwig Boltzmann Institute for Archaeological Prospection and Virtual Archaeology and is a collaboration with the University of Bradford, the University of St Andrews, and the ‘ORBit’ Research Group of the Department of Soil Management at the University of Ghent, Belgium.
The data collection technologies include surface remote sensing methods such as aerial photography, laser scanning and airborne imaging spectroscopy. The geophysical prospection methods used ground penetrating radar (GPR), electromagnetic induction, and magnetometry. Under suitable ground conditions GPR surveys provide detailed three dimensional in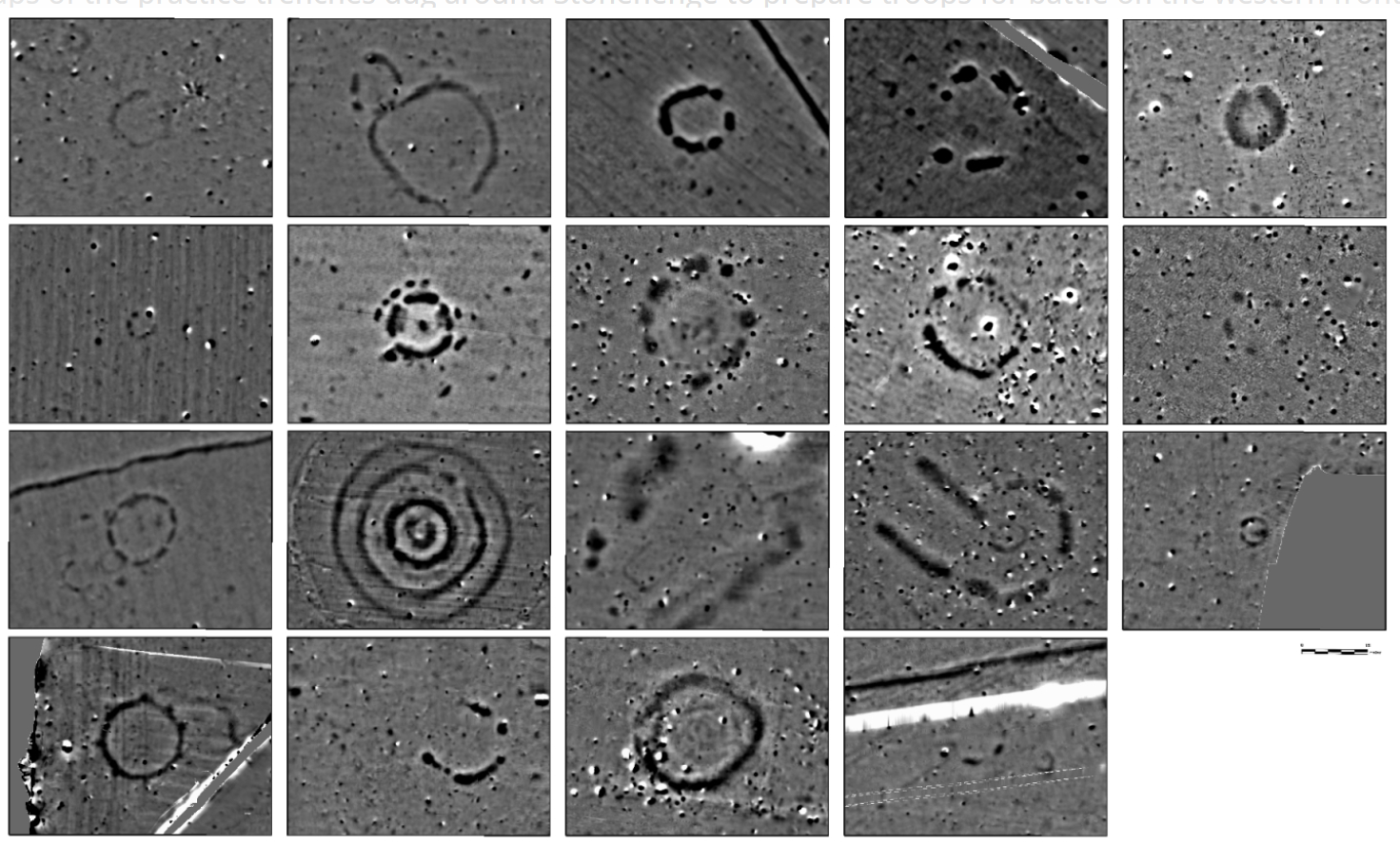 formation about depth, shape and location of archaeological structures at a high spatial resolution. GPR can be used to detect stone structures, interfaces caused by pits and trenches, and cavities and differences in soil humidity. New multichannel GPR arrays permit considerably increased spatial coverage with greatly improved resolution and can generate detailed 3D images of subsurface structures. Magnetometery is most suitable for mapping archaeological structures causing anomalies in the Earth’s magnetic field such as prehistoric pits, trenches, postholes, walls, fire places and kilns. Magnetometer surveys result in a 2D map without direct information about the depth of the buried structures. Electromagnetic induction measurements can be used to efficiently and non-invasively to map physical properties of the soil and buried objects.
formation about depth, shape and location of archaeological structures at a high spatial resolution. GPR can be used to detect stone structures, interfaces caused by pits and trenches, and cavities and differences in soil humidity. New multichannel GPR arrays permit considerably increased spatial coverage with greatly improved resolution and can generate detailed 3D images of subsurface structures. Magnetometery is most suitable for mapping archaeological structures causing anomalies in the Earth’s magnetic field such as prehistoric pits, trenches, postholes, walls, fire places and kilns. Magnetometer surveys result in a 2D map without direct information about the depth of the buried structures. Electromagnetic induction measurements can be used to efficiently and non-invasively to map physical properties of the soil and buried objects.
The main platform for integrating the remote-sensed and the geophyical measurements is a GIS-based archaeological information system, with additional tools for dynamic visualization and spatial analysis. The huge amount of data generated by the remote sensing and geophysical prospection measurements require appropriate data processing, aanalytical and 3D visualization tools.
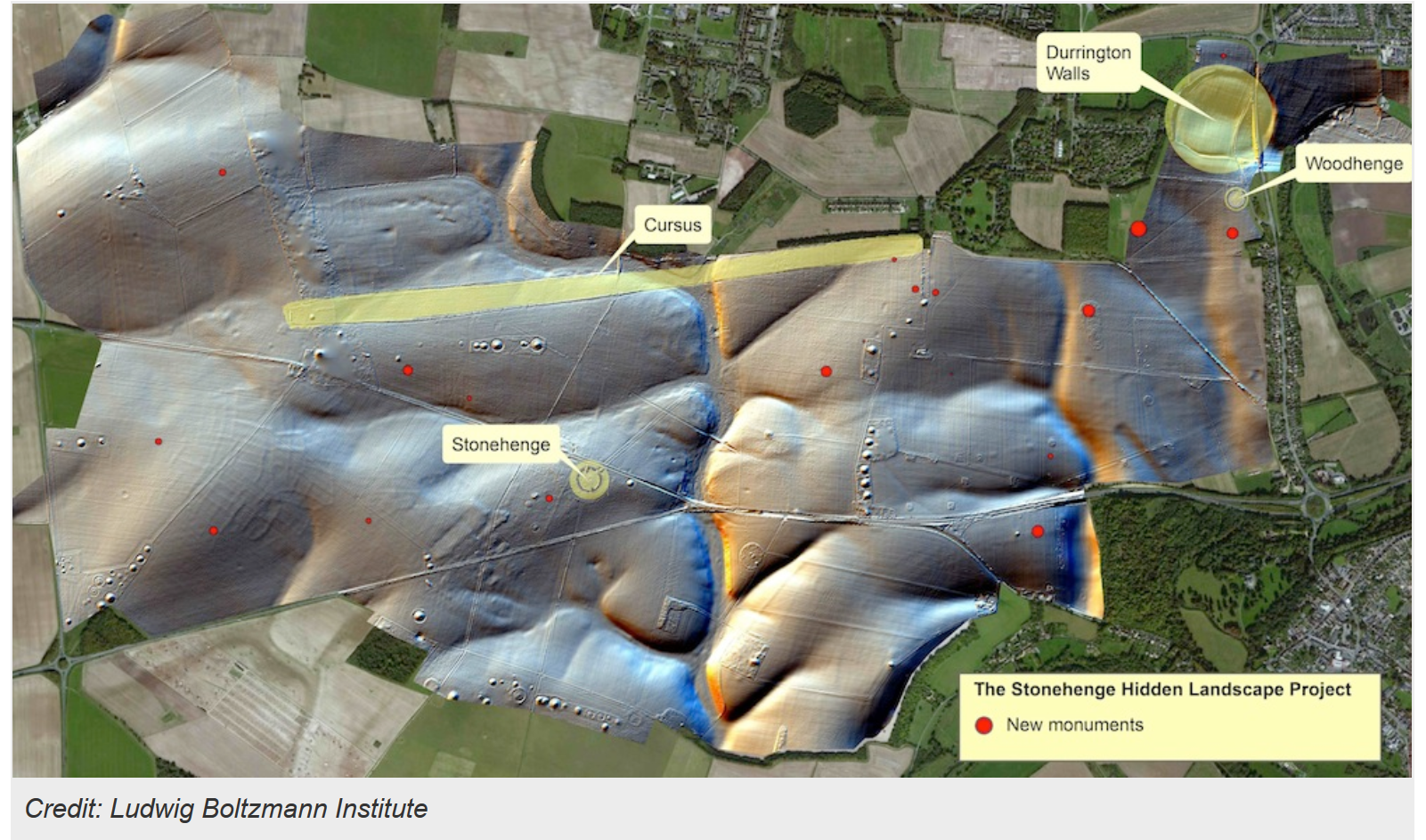 The remote sensing techniques and underground geophysical surveys have discovered hundreds of new features which now form part of the most detailed archaeological digital map of the Stonehenge landscape ever produced. The results of the survey include 17 previously unknown ritual monuments dating to the same time period as Stonehenge. A massive timber building, probably used for the ritual inhumation of the dead and which was finally covered by an earthen mound has been mapped. The immense Durrington Walls ‘super henge’, situated a short distance from Stonehenge was also mapped. It was found to have a circumference of more than 1.5 kilometers. The results will be featured in a new BBC Two series titled Operation Stonehenge: What Lies Beneath.
The remote sensing techniques and underground geophysical surveys have discovered hundreds of new features which now form part of the most detailed archaeological digital map of the Stonehenge landscape ever produced. The results of the survey include 17 previously unknown ritual monuments dating to the same time period as Stonehenge. A massive timber building, probably used for the ritual inhumation of the dead and which was finally covered by an earthen mound has been mapped. The immense Durrington Walls ‘super henge’, situated a short distance from Stonehenge was also mapped. It was found to have a circumference of more than 1.5 kilometers. The results will be featured in a new BBC Two series titled Operation Stonehenge: What Lies Beneath.


Be the first to comment