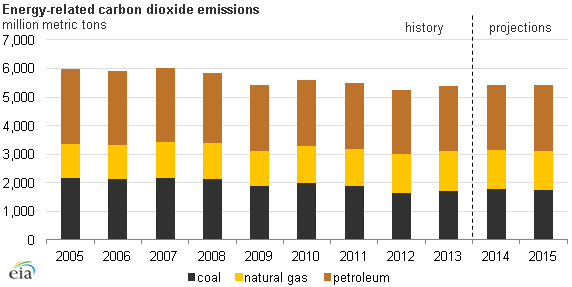
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) energy-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions in 2013 are expected to be 2% above the 2012 level. The EIA ascribes this to a small increase in coal consumption in the electric power sector.
However, emissions in 2013 are more than 10% below 2005 levels. This level of reduction is expected to continue through 2015, according to EIA’s most recent Short-Term Energy Outlook. The administration has committed to a 17% reduction in emissions from the 2005 level by 2020.
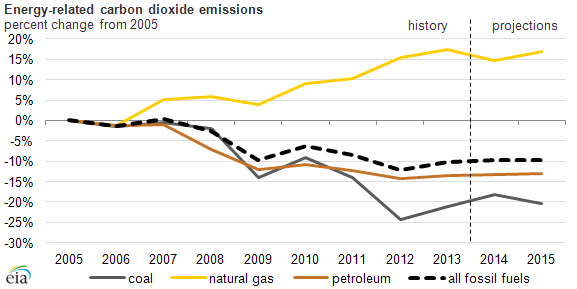 CO2 emissions from energy have declined most years since 2007 which as the U.S. emissions peak. From 2005 to 2013, the most important factors that are changing energy usage in the U.S. are
CO2 emissions from energy have declined most years since 2007 which as the U.S. emissions peak. From 2005 to 2013, the most important factors that are changing energy usage in the U.S. are
- Weak economic growth in the last few years
- Continuously improving energy efficiency across the economy, including buildings and transportation
- High energy prices over the past four years (with the exception of natural gas)
- An abundant supply of natural gas and low prices due to increasing shale-gas production
- Natural gas and renewables displacing coal
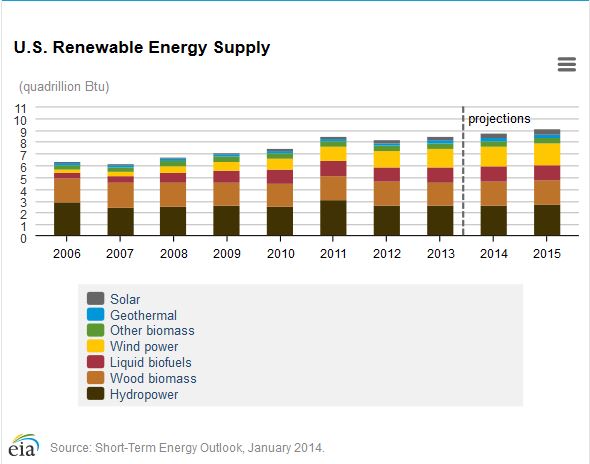 The EIA Short-Term Energy Outlook projects that renewables used for electricity and heat generation will grow by 3.0% in 2014 and by 4.7% In 2015.
The EIA Short-Term Energy Outlook projects that renewables used for electricity and heat generation will grow by 3.0% in 2014 and by 4.7% In 2015.
EIA estimates that wind capacity will increase by 8.8% in 2014 to about 66 gigawatts (GW) by the end of the year and will increase 14.6% to total more than 75 GW at the end of 2015. Electricity generation from wind is projected to contribute more than 5% of total electricity generation by the end of 2015.
EIA currently projects that utility-scale solar capacity will increase by approximately 40% between year-end 2013 and year-end 2015, with photovoltaic (PV) capacity accounting for about 85% of that growth.
EIA projects that solar PV electric capacity will continue to grow in 2014 and 2015 in both the electric power and end-use sectors, and will dominate growth in solar thermal electric capacity, due in part to significant reductions in the price of solar PV panels in recent years.


Be the first to comment