
- NASA’s SWOT Satellite Reveals the Most Detailed Maps of Earth’s Seafloor Yet
- Pakistan Enters a New Space Era with the Launch of Its First Hyperspectral Satellite
- Human Judgment Remains Central in the Era of Geospatial Artificial Intelligence
- EU-Wide Real-Time Drone Detection & Registration Network Proposed to Counter Hybrid Threats
- Airbus, Leonardo and Thales Sign MoU to Establish a Leading European Space Champion
- United States Adopts Version 3.0 of National Ecosystem Classification Standard
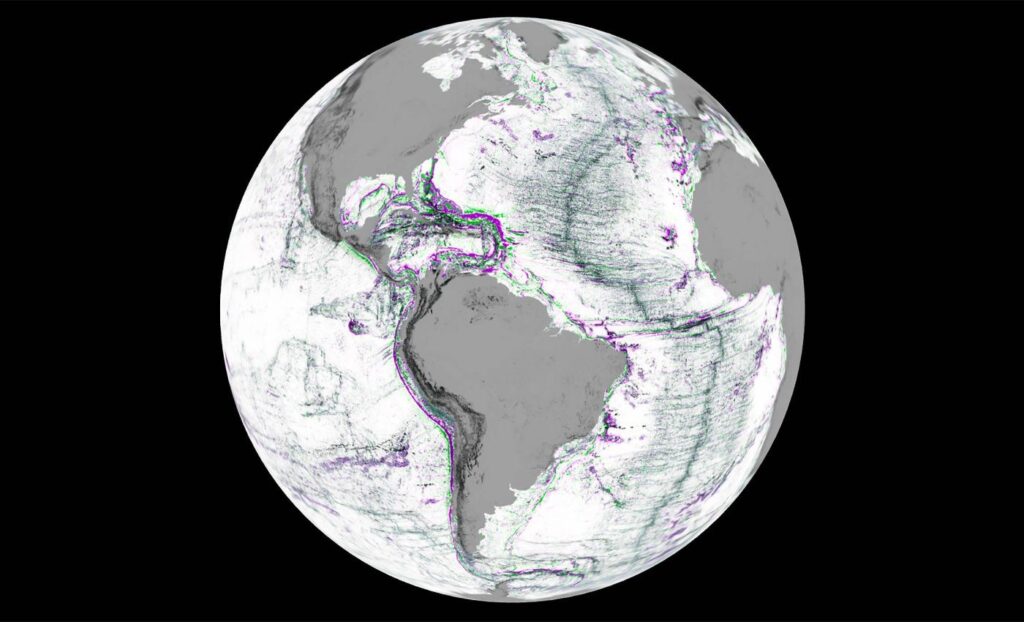
NASA’s SWOT Satellite Reveals the Most Detailed Maps of Earth’s Seafloor Yet
NASA and the French space agency CNES, has produced highly detailed maps of the Earth’s seafloor. NASA’s SWOT satellite is designed to measure the height of water surfaces across 90% of the planet every three weeks, it captures subtle ripples caused by hidden underwater mountains and ridges.
These detailed maps allow scientists to reconstruct the shape of the seafloor with unprecedented precision. The result is a global map that reveals unseen ocean structures, guiding everything from submarine cable routes to climate models. Though ship-based sonar still provides the most accurate depth data, SWOT’s view from space fills the vast blank spaces of our oceans, illuminating the mysterious world beneath the waves. Read more here.
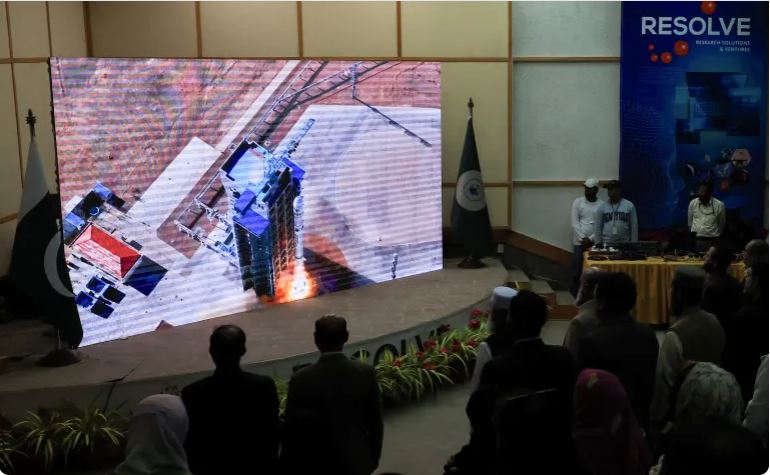
Pakistan Enters a New Space Era with the Launch of Its First Hyperspectral Satellite
For the first time, Pakistan can now see its land, water, and cities through hundreds of spectral lenses, each revealing hidden details of soil health, vegetation stress, and water purity. Developed by SUPARCO in partnership with China, Pakistan’s first hyperspectral satellite—HS-1 is a powerful eye in the sky marks a leap toward smarter agriculture, resilient infrastructure, and sustainable development across the region. Beyond its scientific potential, HS-1 symbolizes Pakistan’s growing presence in the global space community. Read more here.

Human Judgment Remains Central in the Era of Geospatial Artificial Intelligence
As geospatial analytics increasingly incorporates artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, the assumption that automated systems can fully replace human expertise is challenged. According to recent analysis, while AI tools facilitate object detection, high-resolution mapping, and predictive modelling, their effectiveness depends critically on the human tasks of data preparation, bias correction, model training, and contextual validation.In short, the most effective geospatial platforms will be those that integrate AI’s computational power with human oversight rather than attempting to bypass it. Read more here.

EU-Wide Real-Time Drone Detection & Registration Network Proposed to Counter Hybrid Threats
On 22 October 2025, Belgium proposed the establishment of a pan-European Union real-time network designed to link drone operator registrations with live detection systems across member states.The initiative aims to enable authorities to instantly distinguish legitimate unmanned aircraft operations from unregistered or potentially malicious flights, thereby reinforcing air-space security and mitigating hybrid threat scenarios. Read more here.

Airbus, Leonardo and Thales Sign MoU to Establish a Leading European Space Champion
Airbus, Leonardo and Thales entered into a Memorandum of Understanding aimed at forming a new European space-industry leader. The proposed entity will combine the space systems manufacturing and services capabilities of the three firms (excluding launchers), aiming to enhance Europe’s strategic autonomy, competitive strength in global space markets, and innovation capacity. Read more here.
United States Adopts Version 3.0 of National Ecosystem Classification Standard
NatureServe, in partnership with the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the U.S. Forest Service (USFS) and the Ecological Society of America (ESA), announced the release of Version 3.0 of the U.S. National Vegetation Classification (USNVC), the official standard for classifying and mapping terrestrial ecosystems across the United States.
This update introduces aligned global biome concepts, peer-reviewed mid-level units, and finer-scale local associations that brings greater consistency, compatibility and practical utility across federal, state and academic applications.
By aligning with international frameworks such as the Global Ecosystem Typology and providing enhanced interactive mapping tools, the standard strengthens the ability of conservation, land-management, and natural-resource professionals to deliver harmonized, actionable ecosystem data. Read more here.






Be the first to comment