
According to Esri, a geocode transforms a description of a location to a real location on the Earth. The description can be an address, coordinates, or a name of a place. It is an essential attribute for mapping or spatial analysis. A location-based service is mainly relying on the quality of geographical data and information, therefore there is a strong urge to develop a spatial index system that can locate someone or something quickly and precisely. Various solutions are currently available in the market and some of them are adopted by government institutions and navigation companies for different services.
Limitation of postal code
There are lots of geocode systems available for different purposes. The key component of all those solutions is the accuracy of locations. The postal code system is one of the earliest geocode system used to identify locations since the 1960s. It was originally designed for mailing purposes, but eventually used as a geographic locator to target specific population for different purposes.
Since the irregular shapes of postal code are only optimized for mail delivering, these shapes do not generate meaningful outcome for spatial analysis or positioning practices. For instance, it is not possible to locate a residential unit by postal code only without knowing the street address. Moreover, it cannot be used for spatial analysis to understand distribution of household income when the postal code area is too large.
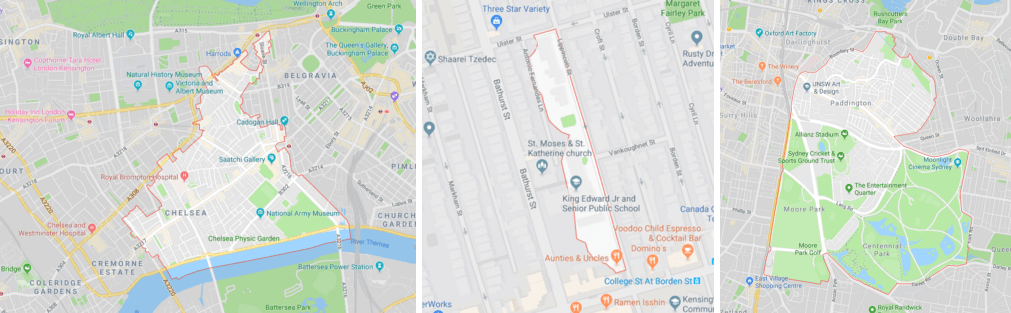
The shapes of postal code are often irregular and unfavorable for analysis.
Photo courtesy: Matt Forest
Different types of spatial indexing
Discrete Global Grid System (DGGS) is a series of discrete global grids. It can be composed by hexagonal- , triangular- , or square-based cells. Regular DGGs are unbiased in terms of spatial patterns. One of the common example for hexagonal DGGS is Uber’s H3 grid system. It is designed to optimize spatial analysis regarding to consumer behaviors because all nearby cells have the same distance and size. It has its own representation, which transforms latitude, longitude and grid resolution into indexes. Meanwhile, the geographic coordinate system, such as the Universal Transverse Mercator coordinate system, is one of a common example of square-based DGGS.
Both applications mentioned above use geographical coordinates in terms of decimal degrees or degree, minute and second, however such expressions involve two groups of numbers that are hard to be memorized and often misread. As a result some alternatives are developed to simplify the spatial index system.
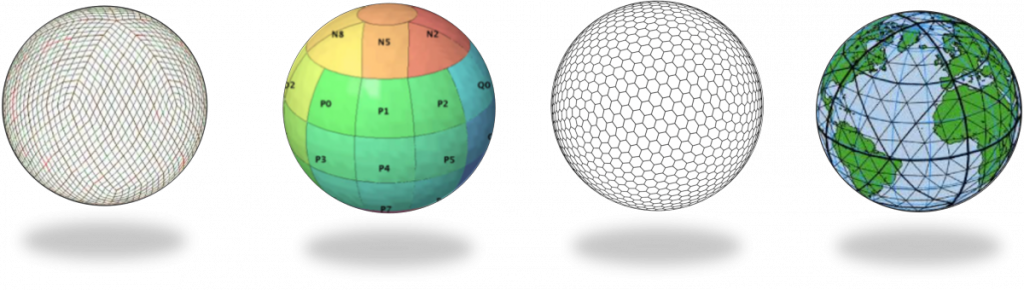
Different types of DGGS.
Photo courtesy: Pyxis
What3words grid system
Imagine when you want to meetup with your friends at the East Block of the Canadian Parliament Hill in Ottawa for a guided tour, its postal code or the street address will only bring you to the main entrance at Wellington Street. Geographical coordination expressed in latitude and longitude can be used to pinpoint the building entrance, but it is inconvenient and easy to misread. The geocode app what3words is designed to describe locations in simple form, especially for areas that are not reached by roads.
What3word’s grid system is composed by 3 meter squares. Each 3×3 grid is assigned with a unique combination of three words without repeating. All GNSS coordinates are simply converted into 3 word database as a new addressing format. Our Earth is not a small planet and 57 trillion squares are needed to cover the entire world. The application is targeted to assist existing mapping solutions for better positioning accuracy. Since it covers anywhere in the world, it allows users to located themselves even in remote areas without identical landmarks nearby. For instance, the 911 service center can easily locate lost people with the 3 word code.
The limitation of this system is that all the wordings are generated randomly without correlation. It is only practical for pinpointing location without any capability for spatial analysis. Another drawback of the application is that the 3 word address can only be transformed into GNSS coordinates but not the street address.

What3word’s 3×3 grid can locate areas without street address for emergency dispatch.
Photo courtesy: What3words
Application of what3words
What3words is becoming more popular in Canada. More than thirty emergency service providers in Canada are now using this application to assist rescue works, and the complete list can be found here. For instance, a rescue team was able to locate a snowmobile crash that was six kilometers away from the closest road. The app will work without internet, therefore the location tag can still be told to 911 dispatchers.
Apart from emergency dispatch, the grid system can also be used to assist in navigation systems. The Mercedes-Benz Canada has integrated what3words to its own navigation system which supports voice input. It avoids positioning mistakes caused by duplicate street names or locations that do not have an address, for example a specific entrance in the park.
The three word code can be recognized easily for voice navigation.
Video courtesy: Mercedes-Benz Canada
Alternatives
Google’s Plus Codes use the same approach as what3words to divide the Earth into small grids based on latitude and longitude coordinates. It is a native plugin that can be found in Google Maps app. The code is composed with 11 characters based on the block size and its distance from the South Pole and the anti-meridian. It can also simplified to a “6 character + City” format.
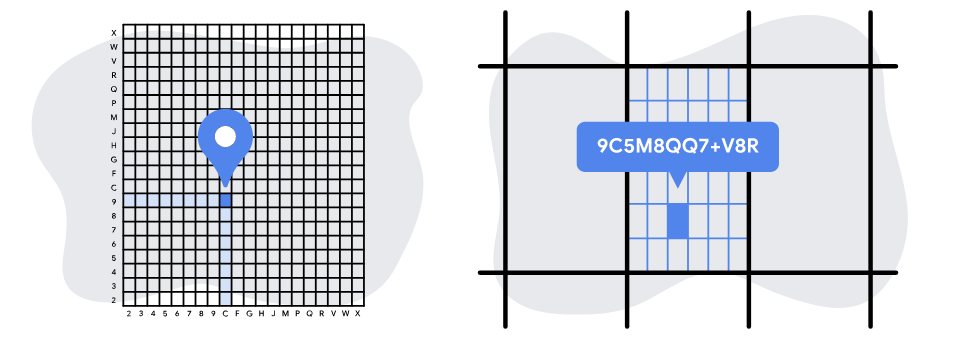
The Plus Codes are formed based on WGS84 coordinates and the size of blocks.
Image courtesy: Google
Although Google’s location code is a great innovation which is fully integrated with Google map, what3words outruns google because of its simplicity and the 3 word codes are more memorable. The Plus Codes work perfectly in a computer environment, however the long combinations of characters may cause misunderstanding during an emergency phone call.
Convenient is the key factor to make a map product popular, as everyday users may not want to deal with complex codes and understand how the system works. What3words is not a all round positioning solution but it can speed up the searching process in order to reach the specific location.
Further Reading
https://www.everycrsreport.com/reports/RL33488.html
https://cdnsciencepub.com/doi/full/10.1139/geomat-2018-0008
https://support.what3words.com/en/
https://www.vicnews.com/news/rcmp-now-using-app-to-track-people-lost-injured-in-b-c-s-backcountry
https://www.gpsworld.com/here-integrates-what3words-into-in-car-navigation-feature/




Be the first to comment